Design Youtube Streaming | Video Transcoding | Delivery
Youtube streaming design: video uploads, transcoding and adoptive bitrate streaming
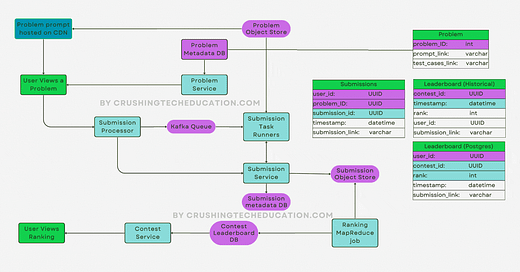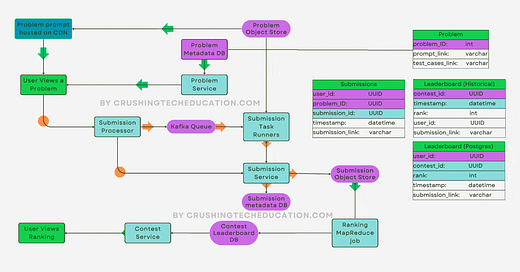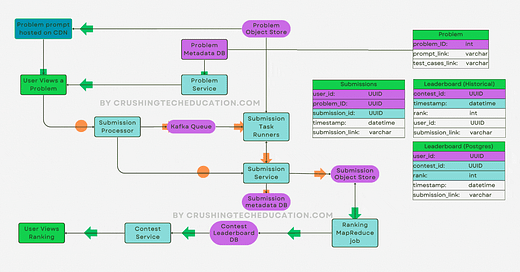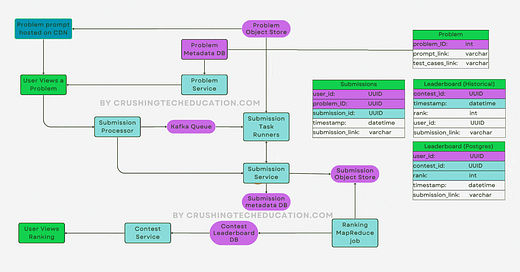
YouTube's streaming system is a sophisticated platform that leverages a variety of streaming protocols, codecs, and container formats to deliver video content efficiently and effectively to a global audience. Understanding these components is crucial for grasping how YouTube manages to stream vast amounts of video content seamlessly across different devices and network conditions.
Video Streaming on YouTube
YouTube's streaming technology is sophisticatedly adaptive, meaning it automatically adjusts the quality of the video based on the viewer’s current internet speed and device performance. This adaptability is essential to provide a buffer-free experience across various devices, from smartphones to desktop computers. This system employs complex algorithms to ensure efficient data buffering and playback, enabling users to enjoy their viewing experience with minimal interruptions.
Furthermore, YouTube has implemented technologies such as progressive download and adaptive bitrate streaming. Progressive download allows the video to be played while it is still downloading, improving the user experience by reducing wait times. Adaptive bitrate streaming, on the other hand, dynamically adjusts the video quality in real-time based on the viewer's internet bandwidth and device capabilities, ensuring the best possible quality with the available resources.
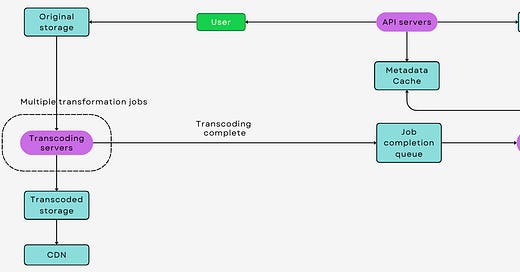
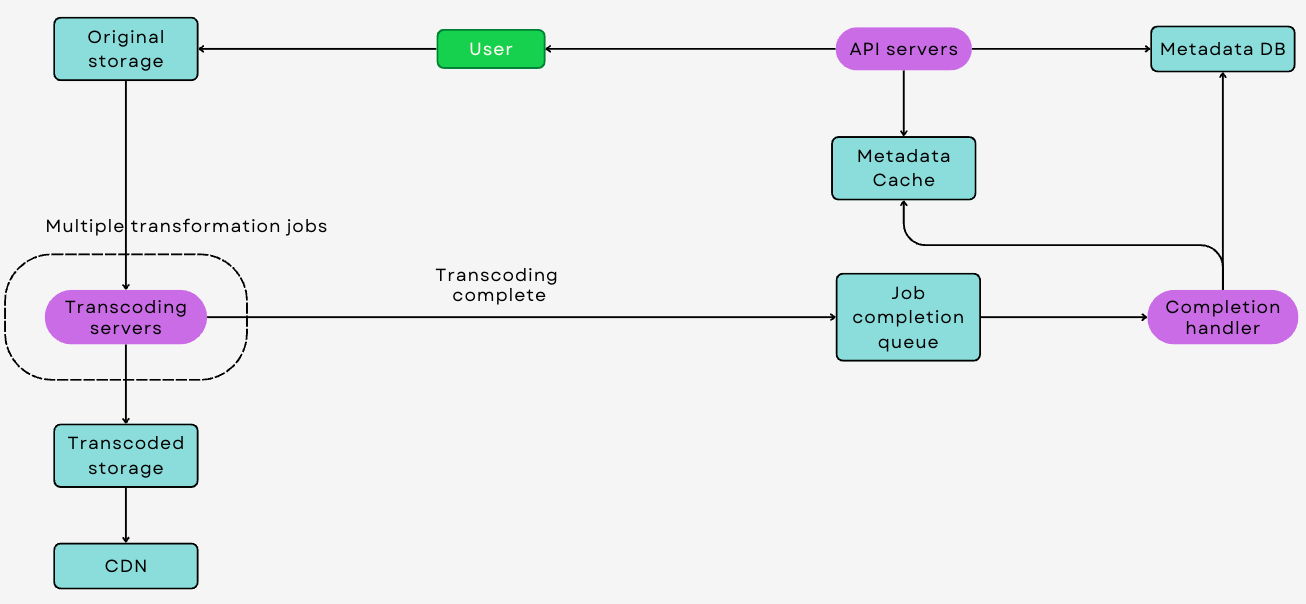
How YouTube's Transcoding System Works
When a video is uploaded to YouTube, it undergoes a complex process of analysis and transformation. The original file is first analyzed for its format, resolution, bitrate, and other technical specifications. Based on this analysis, the transcoding system decides how to best convert the video for optimal streaming. The transcoding process involves several steps:
Resolution and Bitrate Adjustment: Videos are transcoded into multiple resolutions and bitrates. This includes creating lower-resolution versions for users on slower internet connections and higher-resolution versions for those with faster connections and more capable devices. For instance, a single video may be available in 360p, 720p, 1080p, and even 4K resolutions, each with appropriate bitrates.
Format Conversion: YouTube's transcoding system converts videos into formats that are broadly compatible and efficient for streaming. The widely used formats include H.264, VP9, and more recently, AV1. These codecs are known for their ability to compress video data effectively without significant loss in quality, making them ideal for internet streaming.
Adaptive Streaming Preparation: Transcoding prepares videos for adaptive bitrate streaming, a technology that allows the streaming quality to adjust in real-time based on the viewer's internet speed. This is achieved by segmenting the video into small chunks, each encoded at different quality levels.
Streaming Protocols
At the heart of YouTube's streaming system are streaming protocols, which are sets of rules governing how data is transmitted over the internet. The most prominent protocol used by YouTube is HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). Developed by Apple, HLS is widely supported and flexible, making it ideal for a platform like YouTube that serves a diverse range of devices, from smartphones to smart TVs. HLS works by breaking down the video into small, downloadable chunks, allowing for efficient transmission and adaptive bitrate streaming. This means that the video quality adjusts dynamically based on the user's internet speed, ensuring a buffer-free experience. Another key protocol in use is Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH), which, similar to HLS, allows adaptive streaming. DASH is an international standard and is particularly useful for ensuring compatibility across different platforms and devices.
Codecs
Codecs, which compress and decompress video and audio data, are crucial in reducing the size of video files, making them easier to transmit over the internet. YouTube uses a variety of codecs, but the most notable ones include VP9 and H.264. VP9, developed by Google, is known for its efficiency in compressing video, which is particularly beneficial for reducing bandwidth usage and facilitating faster loading times. H.264, also known as AVC (Advanced Video Coding), is another widely used codec on YouTube. It strikes a balance between compression efficiency and compatibility, as it is supported by almost all modern devices and browsers.
Container Formats
Container formats are another vital component of YouTube's streaming system. These formats encapsulate the compressed video and audio streams, along with other important data such as subtitles and metadata. YouTube primarily uses the MP4 container format, owing to its wide compatibility and support for advanced features like streaming and interactivity. MP4 works well with both VP9 and H.264 codecs, making it a versatile choice for the platform.
Feel free to check a video version with more deep dive content.